
This may be of particular benefit to patients with higher surgical risks, minimizing exposure to treatments that are not only more invasive and expensive, but that can impose greater postoperative risks. Nonoperative methods for closed fractures can sometimes be more safely delivered even with more difficult fractures. CONCLUSIONSīased on the results of this literature review, orthopedic providers should consider the preferable outcomes associated with nonoperative fracture management such as lower infection rates, the possibility of rapid functional improvements and lower healthcare costs. In this paper, the authors review the history of closed extremity fracture treatments, outline contemporary studies regarding treatments of non-displaced fractures, and discuss the recent literature that has informed orthopedic surgeon-patient decision-making discussions regarding closed fracture management. More recently, there has been an increased promotion in the medical literature to evaluate the clinical outcomes of nonsurgical treatment of common upper and lower extremity closed fractures. Over the last 150 years, aseptic technique, anesthesia, antibiotics, and internal implants have changed how orthopedic specialists approach fracture care. Amputation is usually performed only as a life-saving operation for a severe infection that is out of control.Fracture treatment has been documented since the times of ancient Egyptian and Greek civilization, with fracture reduction techniques and the apparatus for immobilization developed over three millennia.
In very rare cases, amputation of the infected limb may be considered. Occasionally, a patient may need to take antibiotics for the rest of their life. It may require long-term antibiotic treatment, as well as several surgeries. Most patients will have to take antibiotics for 6 to 12 weeks.Ī bone infection can be hard to eliminate. An infectious disease specialist may work with your doctor to determine the appropriate antibiotics. Once the type of bacteria is identified, your doctor can choose the most effective antibiotics to treat the infection. Rosemont, IL, American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 2008: pp. Reproduced from Zalavras CG, Marcus RE, Levin LS, Patzakis MJ: Management of open fractures and subsequent complications. Antibiotic delivery systems, like "antibiotic beads," may also be used to provide higher concentrations of antibiotics.Īntibiotic beads, like the ones shown here, can be used to help prevent or treat an infection after a fracture. Special drains may be placed in the wound to help rid it of pus. This stage of treatment may require more than one surgery. During surgery, your doctor will either swab or take samples of the infected tissue to find out what type of bacteria is causing the infection. If you have an infection after surgery, your doctor may initially treat it with antibiotics alone, but you will likely need additional surgery to clean out the infection. Depending on the severity of your injury, you may require several debridement and irrigation procedures. It is suggested that people with open fractures undergo debridement and irrigation as soon as is reasonable, ideally within 24 hours of sustaining the injury. This procedure, called debridement and irrigation, is typically performed in an operating room.
You may also be at greater risk because of the lifestyle choices you make. Risk FactorsĬhronic diseases that lower your immune system may put you at greater risk for infection after fracture. This occurs when bacteria enter the body during another surgical procedure (such as a tooth extraction or root canal) and make their way to the implants used to treat the fracture. Less commonly, an infection can occur at the surgical site even long after the injury has healed.

Preventative antibiotics are given before surgery to lower the risk for infection. The risk for developing an infection in this setting is quite low, usually less than 1% in healthy individuals, although this varies depending on the injury and the operation performed.
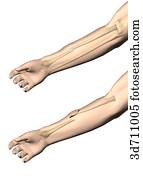
#Open vs closed fracture skin
Surgeryĭuring surgery to fix a fracture, the doctor cuts through skin and soft tissues to reach the broken bone.

Rosemont, IL, American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 2016, pp. (Right) Reproduced from Egol KA, Gardner MJ, eds: Let's Discuss Management of Common Fractures. The broken end of the tibia (shinbone) has torn through the soft tissues and is sticking out through the skin. Illustration and x-ray show an open fracture.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
